Olugbemi. Adeyinka Ogunleye
5 months ago
Olugbemi. Adeyinka Ogunleye
5 months ago
Overview
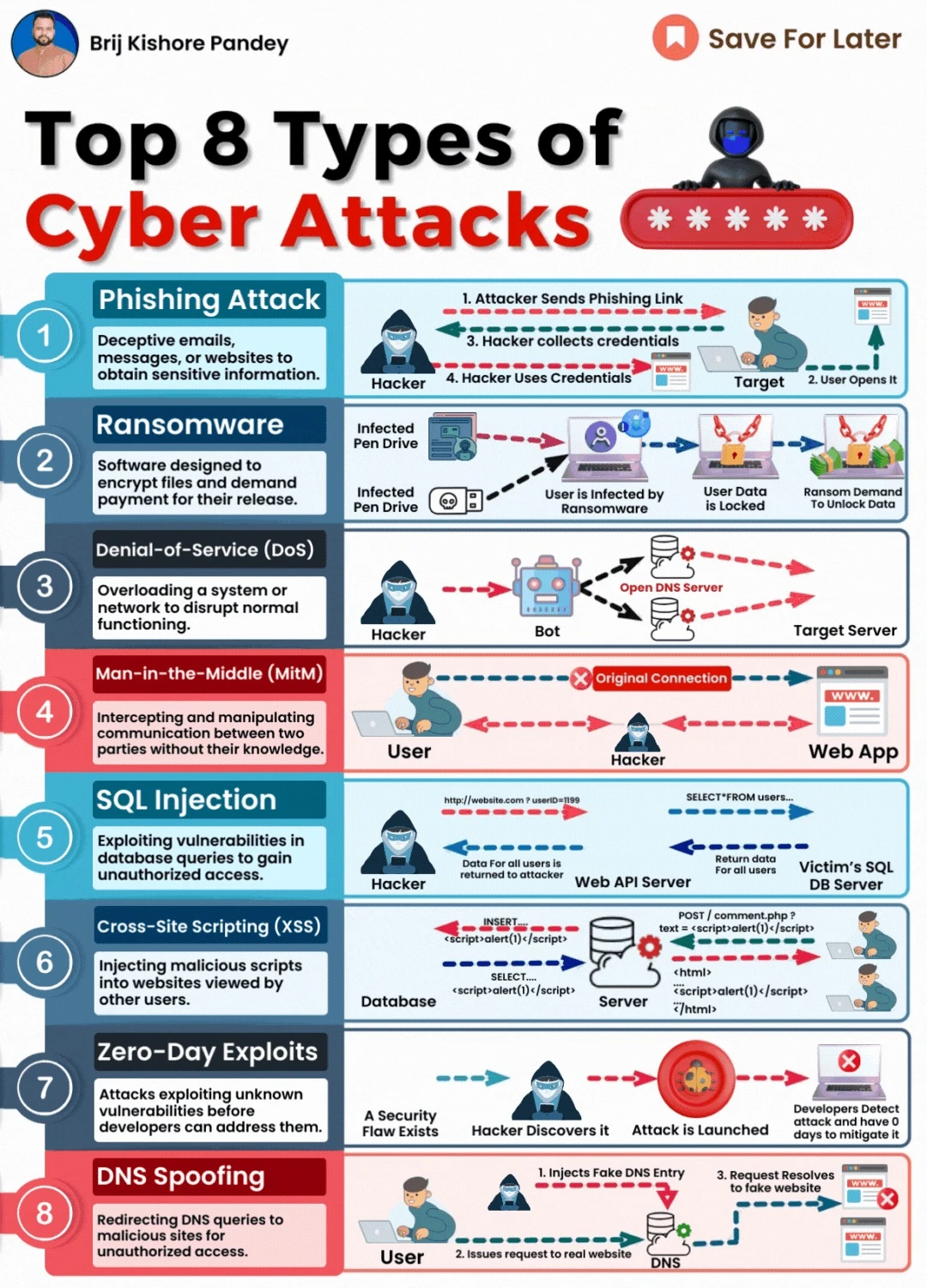
Top 8 Types of Cyber Attacks
As technology becomes the backbone of modern business, understanding cybersecurity fundamentals has shifted from a specialized skill to a critical competency for all IT professionals.
Here’s an overview of the critical areas IT professionals need to master:
Phishing Attacks
- What it is: Deceptive emails designed to trick users into sharing sensitive information or downloading malicious files.
- Why it matters: Phishing accounts for over 90% of cyberattacks globally.
- How to prevent it: Implement email filtering, educate users, and enforce multi-factor authentication (MFA).
Ransomware
- What it is: Malware that encrypts data and demands payment for its release.
- Why it matters: The average ransomware attack costs organizations millions in downtime and recovery.
- How to prevent it: Regular backups, endpoint protection, and a robust incident response plan.
Denial-of-Service (DoS) Attacks
- What it is: Overwhelming systems with traffic to disrupt service availability.
- Why it matters: DoS attacks can cripple mission-critical systems.
- How to prevent it: Use load balancers, rate limiting, and cloud-based mitigation solutions.
Man-in-the-Middle (MitM) Attacks
- What it is: Interception and manipulation of data between two parties.
- Why it matters: These attacks compromise data confidentiality and integrity.
- How to prevent it: Use end-to-end encryption and secure protocols like HTTPS.
SQL Injection
- What it is: Exploitation of database vulnerabilities to gain unauthorized access or manipulate data.
- Why it matters: It’s one of the most common web application vulnerabilities.
- How to prevent it: Validate input and use parameterized queries.
Cross-Site Scripting (XSS)
- What it is: Injection of malicious scripts into web applications to execute on users’ browsers.
- Why it matters: XSS compromises user sessions and data.
- How to prevent it: Sanitize user inputs and use content security policies (CSP).
Zero-Day Exploits
- What it is: Attacks that exploit unknown or unpatched vulnerabilities.
- Why it matters: These attacks are highly targeted and difficult to detect.
- How to prevent it: Regular patching and leveraging threat intelligence tools.
DNS Spoofing
- What it is: Manipulating DNS records to redirect users to malicious sites.
- Why it matters: It compromises user trust and security.
- How to prevent it: Use DNSSEC (Domain Name System Security Extensions) and monitor DNS traffic.
Why Mastering Cybersecurity Matters
- Risk Mitigation: Proactive knowledge minimizes exposure to threats.
- Organizational Resilience: Strong security measures ensure business continuity.
- Stakeholder Trust: Protecting digital assets fosters confidence among customers and partners.
The cybersecurity landscape evolves rapidly. Staying ahead requires regular training, and keeping pace with the latest trends and technologies.